What is the difference of fats and oils?
What is the difference of fats and oils?
Fats and oils make an important contribution to adequate nutrition, they are a source of energy for the body, they insulate and protect the body’s vital organs, they are a source of essential fatty acids and they are required for the absorption of the fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K.
The most obvious and defining difference between fats and oils is that fats are typically solid at room temperature whereas oils are liquid at room temperature.
Fats and oils enter our diet through a variety of sources; dairy products, and meat, fish, poultry and seafood are all sources of fats, and some vegetable and plant foods are sources of oils.
Fats and oils also enter our diet through many of the products we add to our foods to aid cooking or to simply make them more ‘palatable’. Such additions include; butter, margarine, lard, mayonnaise, ghee and cooking oils.
Uses of Oil & Fat :
Oil & Fat are the main nutritional components of human food and important raw material of food processing. Oil Processing is one of the important industries throughout the world. With the rapid development of economy and the continuous improvement of people’s living standard, per capita demand for oil and fat is obviously growing. And the demand for oil quality and nutrition also improve constantly. All these facts make oil refinery a very promising and profitable industry to invest in, pointing out the development direction of edible and cooking oil market.
Fats and oils are used throughout the world for both food applications and industrial uses. They are consumed in butter, shortening, margarine, salad oils, and cooking oils, as well as in animal feeds, fatty acids, soaps, personal care products, biodiesel, paints (made from alkyd resins), lubricants, and greases. The sources of fats and oils include edible vegetable oils, palm oils, industrial oils, animal fats, and marine oils. Food applications account for the major share (about three-fourths) of the worldwide consumption of fats and oils.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of fats and oils:
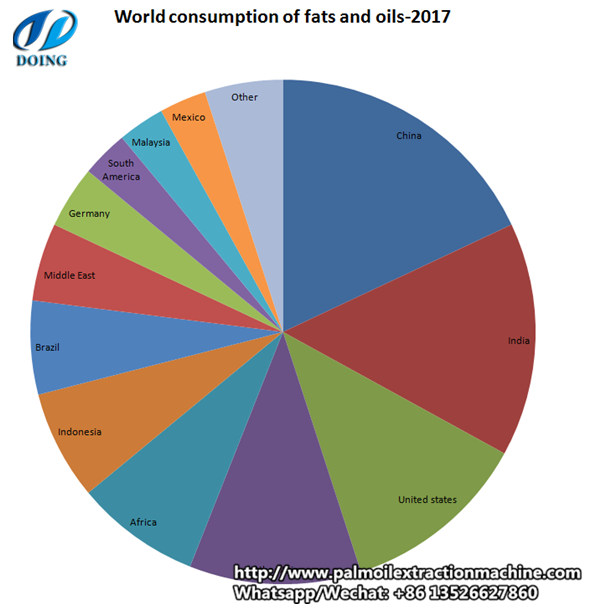 World consumption of fats and oils---2017
World consumption of fats and oils---2017
World consumption of fats and oils is driven mainly by Asia, which accounts for 48% of the world total. China and India together make up 30% of the world total. Chinese demand is mainly for soybean oil, followed by canola and palm oils. India is a major consumer of canola oil, as well as palm oil and butter. Both countries expect continued strong growth. Indonesia and Malaysia also contribute to overall consumption, especially in palm oil demand.
Overall, the fats and oils industry is growing because of increases in population and increased industrial uses. Oils are occasionally substituted for each other in specific market areas in reaction to long-term trends affecting price or consumer perception of the individual oils.
What is the oil content of main Oil & Fat?
Different oil & fat have different oil content. The following form show us the oil content of main vegetable oil:
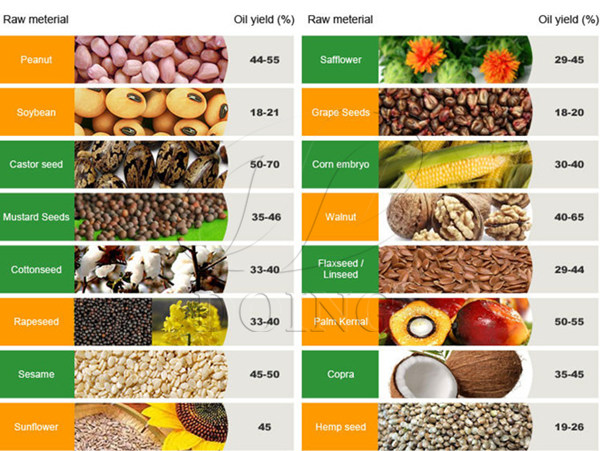 Oil content of main oil & fats
Oil content of main oil & fats
Vegetable oil and animal oil are the two main produces of oil expelling and extracting. Referring to vegetable oils, there are a lot of oil materials, including peanut seeds (groundnut kernel), sunflower seeds, cottonseeds, copra, palm oil, palm kernel, olive, maize germ, soybean, coconut, rapeseed, sesame, grape seeds, rice bran, avocado and so on. Referring to animal oil, chicken oil is what we want to highlight. But today we mainly introduce the vegetable oil.
Here’s a description of the main types of oils and fats:
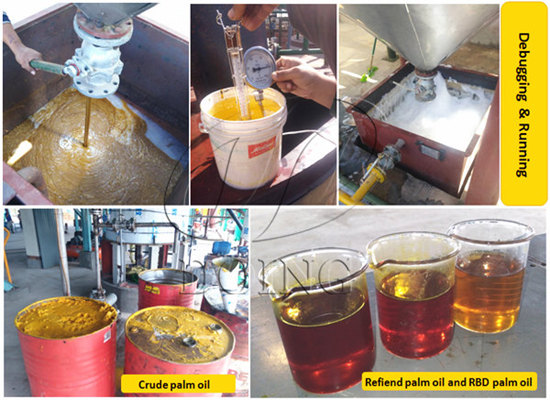
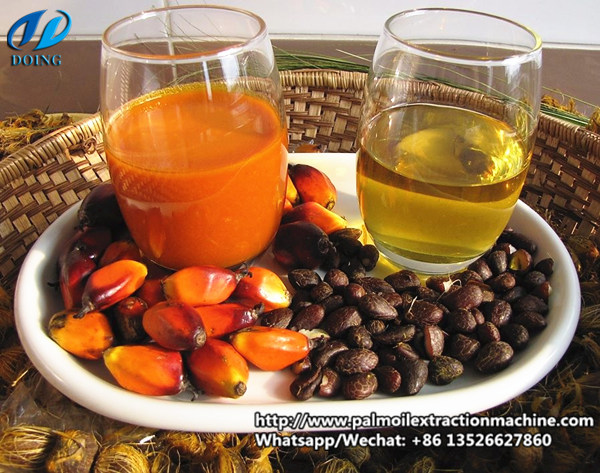
 Crude palm oil
Crude palm oil
Palm oil: Palm oil is the most widely-used vegetable oil in the world. Palm fruit oil, generally known as palm oil, is produced from the pulp of the fruit of the oil palm tree (Elaeis Guineensis). This tropical fruit is reddish in colour because of a high beta-carotene content. The fruit is about the size of a large olive. The fruit has a single seed or kernel, which is used to produce palm kernel oil. Each palm fruit contains about 40-55 per cent oil. Palm fruit oil and palm kernel oil differ significantly in their fatty acid composition, but have the same botanical origin.
Note: Did you know about palm oil?
Palm oil and palm kernel oil represent 38 per cent of the global vegetable oil production.
62 million tons of palm oil is produced annually.
One palm tree produces 40 kilogrammes of palm oil every year.
One hectare of oil palm trees produce on average 3.8 tons of oil each year.
Oil palm accounts for 7 per cent of all the cultivated land for vegetable oils globally, but has the highest output, producing 38 per cent of all oils and fats.
Indonesia and Malaysia supply 85 per cent of the palm oil used globally.
In Indonesia and Malaysia together, approximately 4.5 million people earn a living from palm oil.
The use of palm oil in human nutrition dates back 10,000 years.
 Palm kernel oil
Palm kernel oil
Palm kernel oil: As the name suggests, this oil is derived from the kernel or seed of the fruit in oil palms. It contains more saturated fats than palm oil and is very commonly used in commercial cooking since the higher saturated fat content allows for greater stability at higher temperatures and better shelf life.
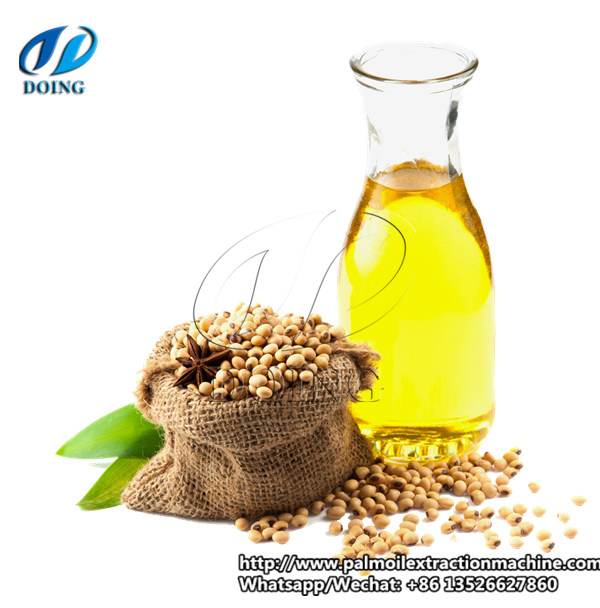 Soybean oil
Soybean oil
Soybean oil : Soyabean oil is a vegetable oil that is extracted from soybeans, which are scientifically known as Glycine max. It is one of the most widely used vegetable oils in the world, possibly because soybeans are some of the most widely cultivated and utilized plants, particularly in recent decades. Soybean is native to East Asia and is considered a legume, however, despite its limited origin; it is highly prized for its edibility. Most soybean oil is refined, blended, and sometimes hydrogenated and it can be graded into different levels and strengths depending on the desired application.
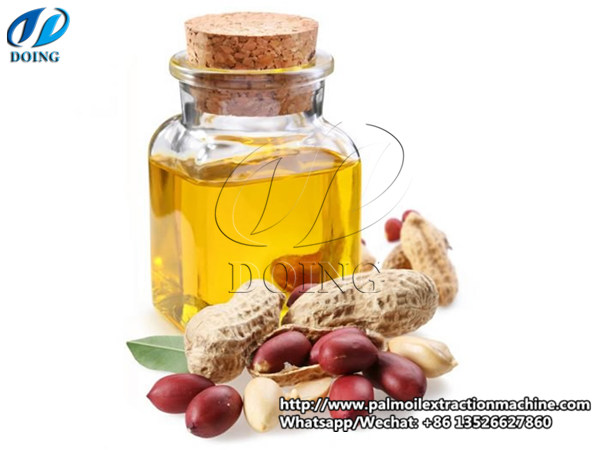 Peanut oil
Peanut oil
Peanut oil: Peanut oil, also known by other names such as groundnut oil and arachis oil, is a type of vegetable oil commonly used in cooking that is derived from peanuts. It comes in a number of varieties, including refined, unrefined, roasted, and cold-pressed, which have slight differences in their nutritional value and health benefits. Generally, people use peanut oil in their cooking for the interesting flavor that it gives, particularly the roasted variety, as well as the fact that it is healthier than many types of oil.
Peanut oil is most commonly used in Asian cultures, including that of China and Southeast Asian nations like Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia.
 Sunflower oil
Sunflower oil
Sunflower oil: Sunflower oil is a non-volatile oil that can be easily extracted from sunflowers. Although most people are already familiar with sunflowers, they don’t immediately think of sunflowers as sources of an extremely healthy vegetable oil that can replace some of the less healthy cooking oils available on the market. Sunflower oil is also used in certain cosmetic applications. The main producers of sunflower oil are Russia, Ukraine, and Argentina, but it is used throughout the world in the preparation of various cuisines.
Sunflower oil has many uses, including the following:
Used in cooking and frying
Used in cosmetics like lip balms and skin creams
Used as a medicine for the heart as it is low cholesterol
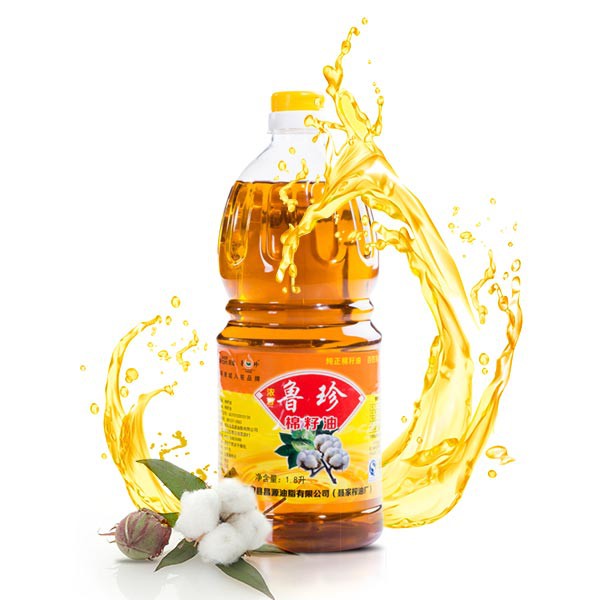 Cottonseed oil
Cottonseed oil
Cottonseed oil: Cottonseed oil is a cooking oil extracted from the seeds of cotton plants. Cotton seed has a similar structure to other oilseeds such as sunflower seed, having an oil-bearing kernel surrounded by a hard outer hull; in processing, the oil is extracted from the kernel. Cottonseed oil is used for salad oil, mayonnaise, salad dressing, and similar products because of its flavor stability.
 Rapeseed oil
Rapeseed oil
Rapeseed oil: Rapeseed, also known as rape, oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae, cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed. It is the third-largest source of vegetable oil in the world. Rapeseed oil also named canola oil is a type of edible cooking oil that most commonly comes from varieties of the rapeseed plant.
 Rice bran oil
Rice bran oil
Rice bran oil: Rice bran oil is the oil extracted from the hard outer brown layer of rice called chaff (rice husk). It is known for its high smoke point of 232 °C (450 °F) and mild flavor, making it suitable for high-temperature cooking methods such as stir frying and deep frying. It is popular as a cooking oil in several Asian countries, including Bangladesh, Japan, India, and China.
 Coconut oil
Coconut oil
Coconut oil: Coconut oil, or copra oil, is an edible oil extracted from the kernel or meat of mature coconuts harvested from the coconut palm (Cocos nucifera). It has various applications. Because of its high saturated fat content, it is slow to oxidize and, thus, resistant to rancidification, lasting up to six months at 24 °C (75 °F) without spoiling.
 Olive oil
Olive oil
Olive oil: Olive oil, as we all know, is an essential fruit oil, which we get from the olive tree crop found mainly in the Mediterranean regions. It has been used by mankind for many centuries. It is utilized for cooking purposes, developing cosmetic products and soaps, for medicinal purposes, and as pharmaceutical supplements. It can also be used as fuel and for lighting lamps.
How to choose the best fats and oils
Many oils are available in local supermarkets, you can choose fats and oils according to your needs. Wherever you shop for them, remember that oils tend to go rancid if not stored properly, so purchase them in a store that keeps them away from direct sunlight and heat.
How to store fats and oils?
Check the labels to see what is advised, but most fats should be stored in the refrigerator if you are not going to use them in a short amount of time. Most oils can turn rancid and thus should be stored in the refrigerator and in dark bottles.
 PREV:How to choose a reliable palm kernel oil refinery plant manufacturers?
PREV:How to choose a reliable palm kernel oil refinery plant manufacturers?
 NEXT:What aspects does influence palm oil refinery plant cost?
NEXT:What aspects does influence palm oil refinery plant cost?
Leave A Message About What is the difference of fats and oils?
palm oil refinery plant projects
Palm oil refining technology FAQ
-
 Crude palm oil refining methods and palm oil refining process flow chart
Crude palm oil refining methods and palm oil refining process flow chart
-
 What is a Palm Oil Refinery?
What is a Palm Oil Refinery?
-
 What is palm kernel oil? How to make palm kernel oil, refined palm kernel oil?
What is palm kernel oil? How to make palm kernel oil, refined palm kernel oil?
-
 How much it will cost to set up a palm oil refinery plant?
How much it will cost to set up a palm oil refinery plant?
-
 How does the palm oil refinery plant works?
How does the palm oil refinery plant works?
-
 What are the different types of small scale palm oil refinery plants available?
What are the different types of small scale palm oil refinery plants available?
-
 A guide to the equipment for crude palm oil refinery
A guide to the equipment for crude palm oil refinery
-
 What steps make up the palm oil refining process?
What steps make up the palm oil refining process?
-
 What equipment does a 10tpd crude palm oil refining plant include and how much is the price?
What equipment does a 10tpd crude palm oil refining plant include and how much is the price?
-
 How poor palm oil deodorization design can affect your profits?
How poor palm oil deodorization design can affect your profits?












